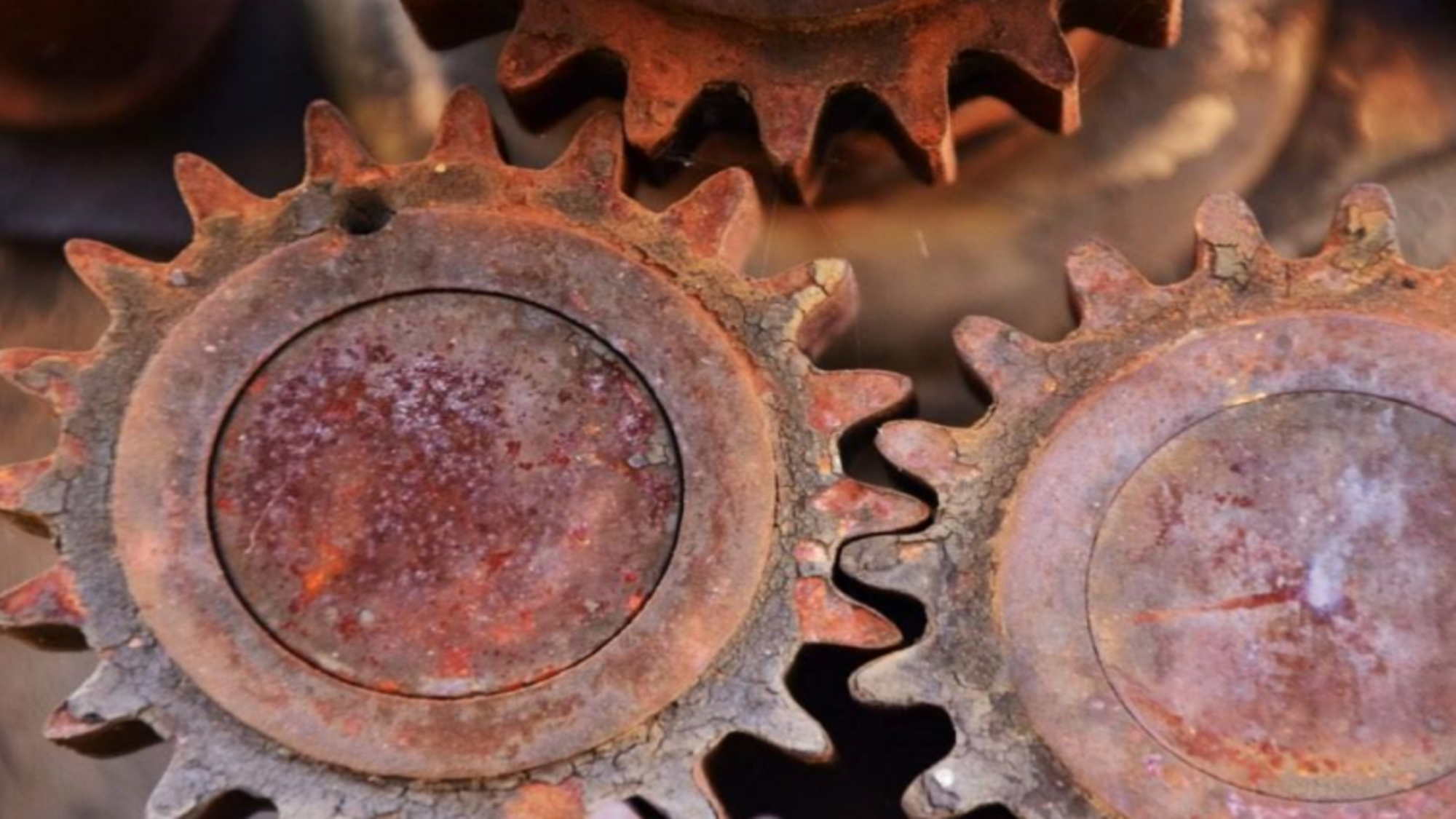
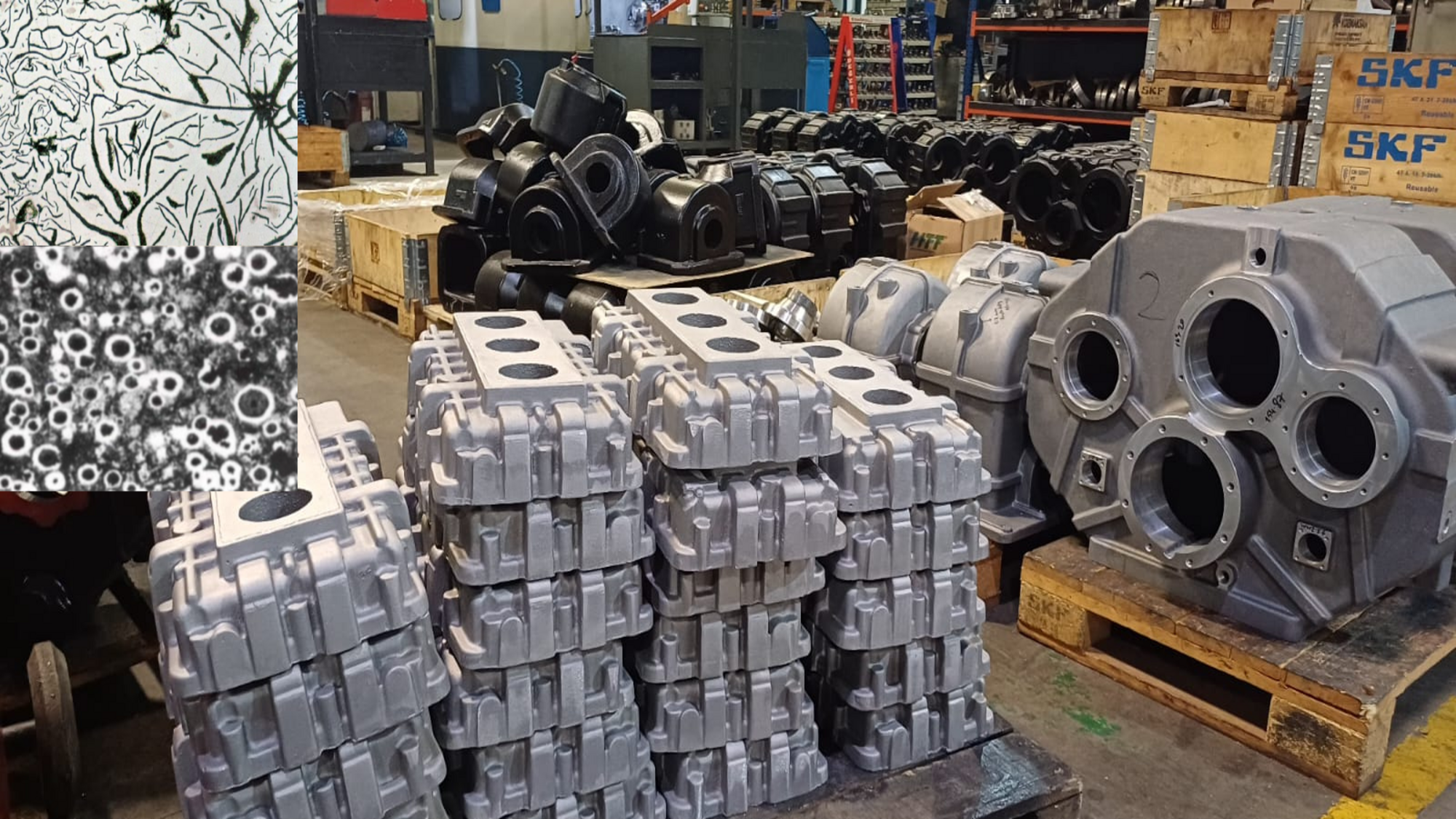
Corrosion Report for steel and gear parts
Corrosion
It means the deterioration of metals and their alloys as a result of chemical and electrochemical reactions with their environment. Corrosion is also defined as the degradation of metals outside mechanical pathways, so that the metal returns to its state in nature. Iron and steel are usually corroded in any environment where oxygen and water are present. The speed of corrosion varies with ambient conditions. For example, it increases with the speed or acidity of water in water, with the increase in temperature or aeration with the movement of the metal, with the presence of certain bacteria or some other effective factors. On the other hand, it is retarded with corrosion protective layers. The alkalinity of water also reduces the corrosion rate on steel surfaces. However, water and oxygen are always required for corrosion to occur. Both determine the amount of corrosion. For example, no corrosion is seen in steels in dry air. If the humidity in the air is below 30, the corrosion is negligible at normal or below normal temperatures.